Display actions
Expand
Entire
Rebin
User_Contour
Use of Marks
Highlight marked area
Project, Profile
ProjectF, Project along function
Project Both
Transpose
Rotate
Superimpose
Show in same range
Show statistics only
Magnify
RedefineAxis
Add new axis
Select Inside
Log scale
Use of marks
Marks are used when expanding and fitting histograms.
They are set pressing the middle mouse button in a
histogram.
If no marks are active the lower and upper edges of the
histogram are used, if only one mark is active the lower
or upper edge is used as the second mark depending on the
position of the InOutSide switch. Marks may be set using
keyboard input. (Set2Marks). They can be converted to
windows. These windows may be written to a workfile to be
used by other programs like cuts in 2dim histograms.
Highlight marked area
Fill the area of a 1-dim histogram between 2 marks with a
selectable color. The fillarea attributes of the generated
TGraph may be changed afterwards invoking the
SetFillAttributes popup menu with the right mouse.
Saving the histogram to a file will also save this area.
Expand
Expand histogram using marks, if only one mark is active
the lower edge is used as the second mark. This builds a
new histogram, under- and overflow bins will be refilled
correctly. Possible active cuts will be applied.
The command Entire shows the full range range again.
Cuts are ignored.
To get only an expanded view move the mouse into the
labels of the wanted axis, the cursor should turn into a
hand with a forefinger, press the left mouse button and
drag the mouse to the required position an release the
button. To get back to the full picture use the command
Entire from the Display popup menu.
Show entire histogram
Show full range of histogram
RedefineAxis
The values of the axis labels may be redefined by
providing new lower and upper limits for the axis. In
this way the picture can reflect a calibrated spectrum.
Note: This only changes the appearance of the picture.
The histogram itself remains unchanged.
For calibration using a non linear function consult this.
ProjectX,Y ProfileX,Y
The commands ProjectX, ProjectY, ProfileX produce projections
resp. profiles on the X or Y axis for a 2-dim histogram.
Active cuts will be applied.
Project along function
ProjectF will project the difference of the Y - values to
the values of a function previously generated by a fit (See
Help on Fitting). The result is the superposition of
slices in X of the 2-dim histogram where each slice is
shifted such that its Y - value equal to the function
value is moved to zero. So the resulting projection on the
Y-axis will be centered at zero.
This allows a banana shaped distribution to be straightened
so the banana shows its real thickness in the Y-projection.
Project on X and Y
The command ProjectBoth produces projections on the
X and Y axis for a 2-dim histogram in the
same picture. The attached figure demonstrates this.
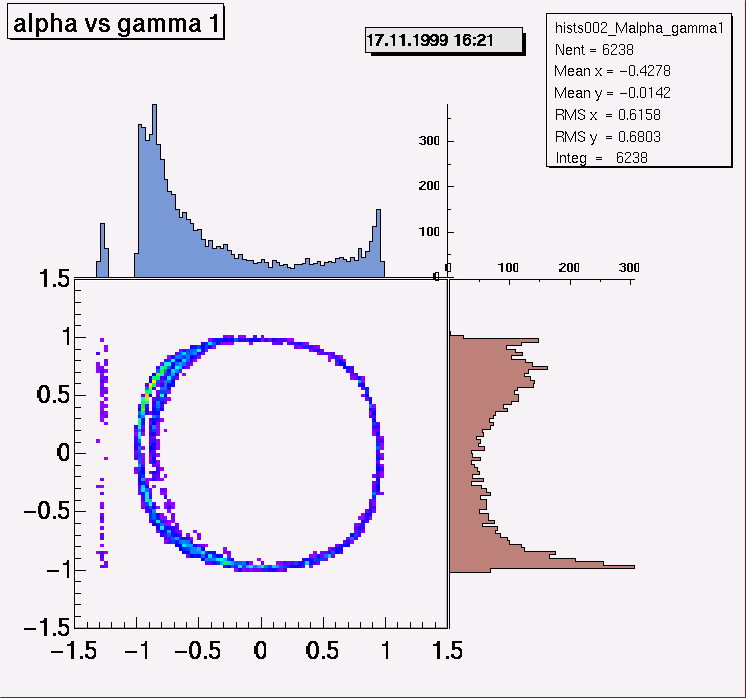
The ratio of the space taken by the scatter plot and the
projections may by adjusted by the parameter
Project_Both_Ratio (see Help_on_Default_Window_Sizes
Transpose a 2-dim histogram
Exchange X and Y-axis of 2-dim histogram.
This is useful together with ProjectF
Rotate a 2-dim histogram
Rotate a 2-dim histogram. This is normally done to align
structures along the X or Y-axis before project or slice
operations.
The determine the rotation angle a pol1 (straight line)
fit to user defined marks should be done before.
Alternativly the angle may be directly given in degrees.
 Note: This is normally only useful if X and Y-axis have the
same scale. The absolute values of the scales are no longer
meaningful.
Note: This is normally only useful if X and Y-axis have the
same scale. The absolute values of the scales are no longer
meaningful.
Show in same range
Show a histogram in same range as this one. If no histogram
is selected a list of histograms in memory is presented
allowing a selection.
Show statistics only
This prints contents, mean, sigma applying active cuts.
Superimpose
Superimpose a histogram on existing picture. A histogram can
be selected from a histogram list by pressing the grey
button left of the name. If none is selected a list of
histograms in memory is presented from which selection can
be done. The latter is needed to show histograms which
result from an operation (scaled, summed etc.). histogram.
For 1-dim the color code is taken from its position + 2
(position 1 gets red etc.) With this command the same scale
is used as for the original histogram.
A command Superimpose scaled is provided for 1-dim hists to
scale the superimposed histogram to the maximum of the
original one in the displayed region.
Magnify
This operation is useful for histograms with many bins.
The (virtual) canvas is extended in such a way that
one bin spans at least 2 pixels on screen. A scrollbar
is added to allow scrolling through the entire picture.
Add new X-Y axis
This allows to add an extra X or Y axis at top or on the
right side of a histogram. The axis range may be choosen
different from the original one.
Select Inside
This option determines if points inside or outside are
choosen when applying cuts.
Log Y, Z scale
This option is added for convenience to choose logarithmic
Y or Z-scale. The same can be achievced from a canvas
popup menu (Right mouse in a canvas outside the borders
of a histogram).
Rebin
Rebin this histogram using the ROOT builtin command. This
command uses the sum of the bin contents. There is an
extended Rebin command provided by HistPresent which
produces a new histogram with sum or avarage of the
bin contents selectable.
User defined contours
Levels and colors in 2-dim histograms using the drawing
options colz or similiar are normally automatically
adjusted using 20 equidistant levels and a color spectrum
blue-green-yellow-red (rainbow colors).
Levels and colors can be selected using Set User Contours
in the Display popup menu. Color numbers or levels
may all be set to 0, in this case the default colors
(e.g. rainbow) and the default equidistant levels are used.
The convention is such that cells with content greater than a
level value and less or equal to the following value get the
corresponding color. That means cells with content below the
lowest level are in background color (not visible).
So in the normal case when no cells with negative content
are present the lowest level should be 0.
These settings can be saved to a rootfile and reused later.
Save is done be the command Save User Contours
Restore is done by selecting the required contour object
in the File list and pressing Use Selected Contours
Clear User Contours establishes the default 20 equidistant
levels again.
This feature is especially useful to get nice logarithmic
contour levels. E.g.: Just define contour levels 1, 10, 100, 1000,
choose log Z-scale and set LogScale_Minumum to 0 if
the bincontents are integer numbers.
Note: With user contours the picture itself will not change
when switching lin - log, only the color palette (Z-scale)
will change.
 Note: This is normally only useful if X and Y-axis have the
same scale. The absolute values of the scales are no longer
meaningful.
Note: This is normally only useful if X and Y-axis have the
same scale. The absolute values of the scales are no longer
meaningful.

 Note: This is normally only useful if X and Y-axis have the
same scale. The absolute values of the scales are no longer
meaningful.
Note: This is normally only useful if X and Y-axis have the
same scale. The absolute values of the scales are no longer
meaningful.